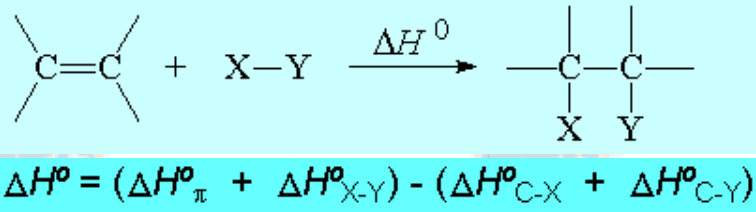A C=C double bond bears a ' pi ' electron cloud from which electrons can be ceded to an electrophilic opponent.
Hence, the most important reaction of alkenes is electrophilic addition.
Addition to alkenes is thus the opposite reaction to elimination leading to alkenes.
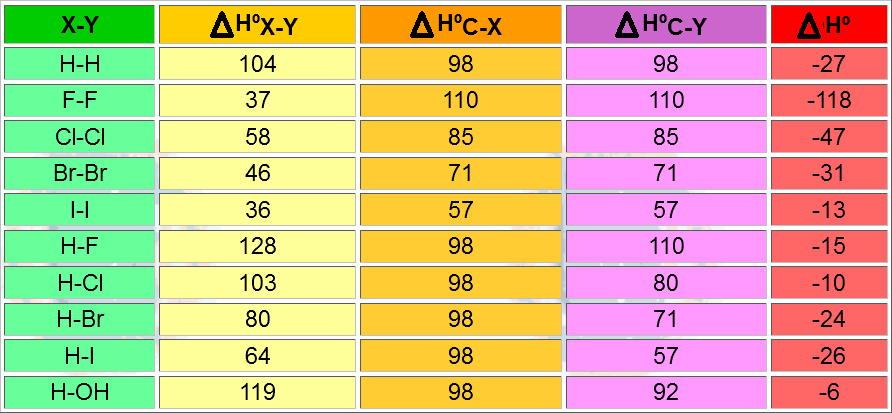
Addition reactions are generally exothermic and therefore thermodynamically favorable. However, they don't usually proceed spontaneously.
If a plausible reaction path exists, i.e. with transition states reasonably high in energy, addition reactions proceed with energy release.