ADDITION OF HYDROGEN, HYDRIDES AND BORANE TO ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
(REDUCTION)
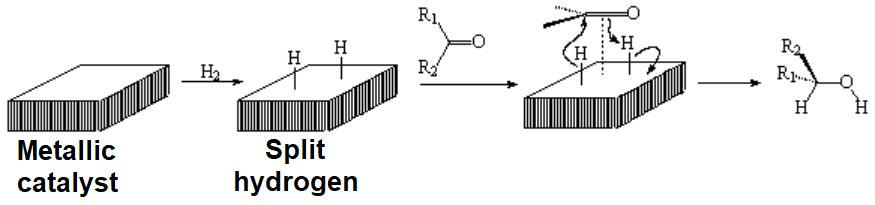
The addition of hydrogen, hydrides or borane to the C=O group of aldehydes or ketones leads to an alcohol and therefore this is an excellent way to preparing the latter.
The reaction is very similar to that studied for the alkenes.
IMPORTANT:
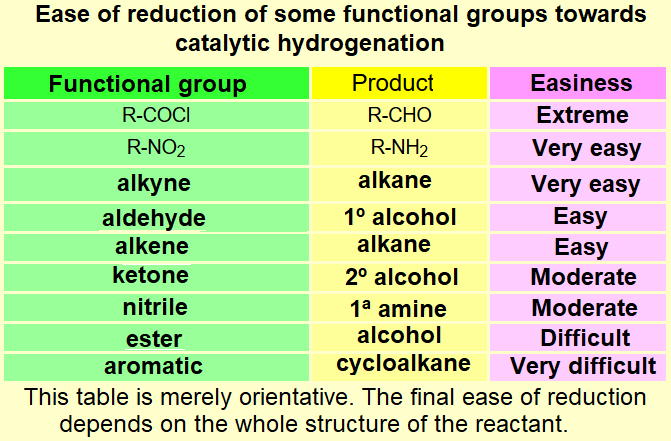
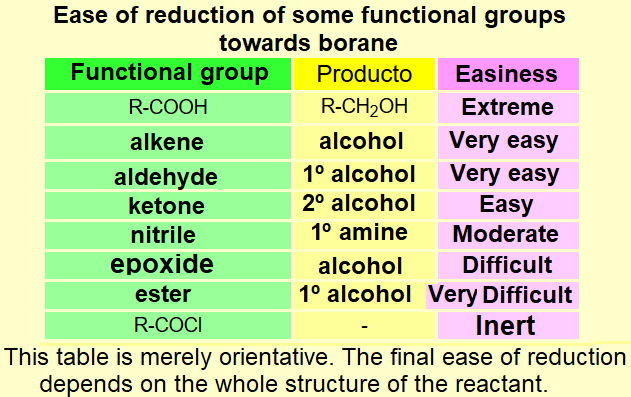
Be careful if there are alkene or alkyne functions in the molecule because they'll get reduced.
Other functions might be reduced too!!!
Peruse the table.
Always be aware of possible competition between the existing functions when attempting a complex synthesis scheme.
Don't forget that the C=O group of aldehydes and ketones can be "protected" against undesired side-reactions.
This reaction was already introduced in the chapter about alcohols as a method for their preparation.
The reaction is very similar to that studied for the alkenes.
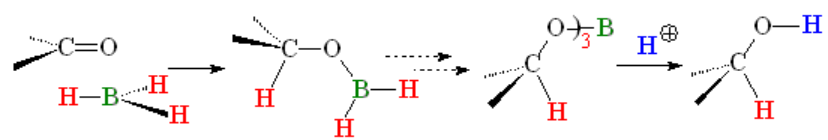
In the case of aldehydes and ketones, the boron atom always ends up bonded to oxygen.
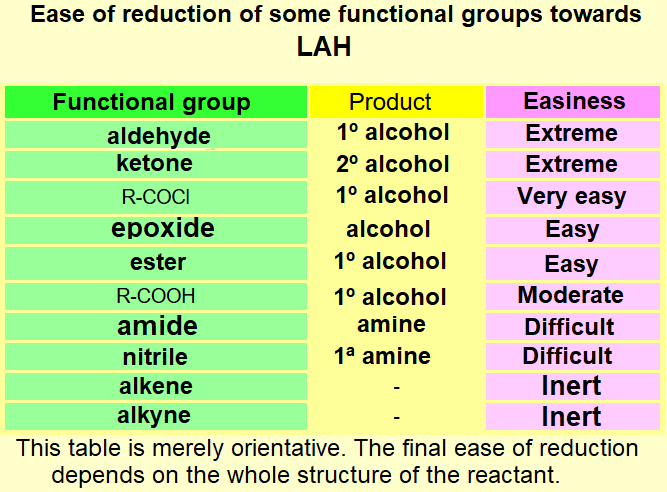
IMPORTANT: Again, DO FOCUS on the possible competition of other functions to boranes.
Please, notice that if you carefully compare the three tables on this page, the reactivity of the different functional groups is quite different.
It is an art your getting around with a chemoselective reduction, i.e. affecting only the function(s) we do choose.
DON'T YOU FRET!!! This is an art that is learned with time, practice and patience.