However, the two electron lone pairs held by the ether's oxygen makes it basic.
Using a strong enough acid, an oxonium ion can be formed.
By heating the reaction mixture, one of the two C-O bonds is broken.
But, which one of the two C-O bonds would break first?
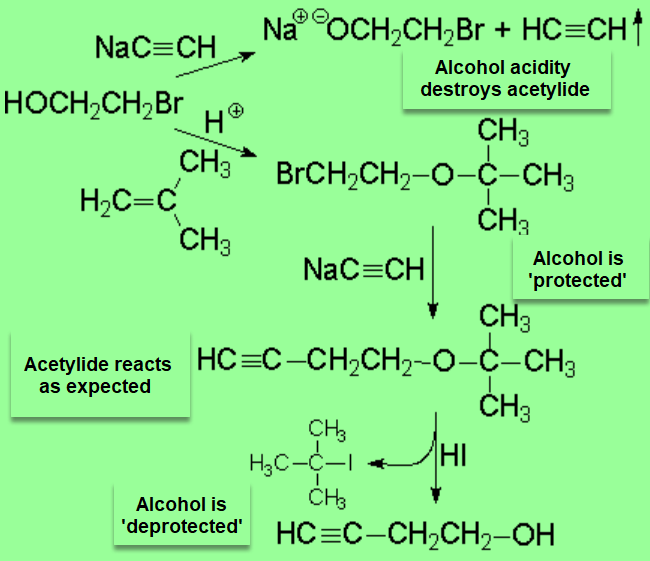 This is an example of a common technique in Organic Chemistry: Protection of functional groups.
This is an example of a common technique in Organic Chemistry: Protection of functional groups.
If we wanted to obtain 3-butin-1-ol from 2-bromoethanol, we wouldn't make it directly react with sodium acetylide because the alcohol, acidic enough, will destroy the nucleophile/base.
In a case like this one, it is mandatory to previously 'protect' the alcohol, by forming the tert-butyl ether, for example.
The ether function is totally inert to the acetylide and does not interfere in the halogen replacement.
The alcohol group is finally recovered by treatment of the ether with HI.
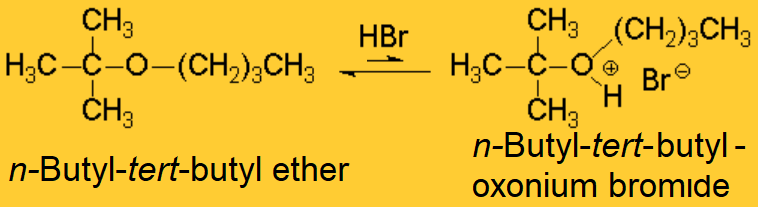
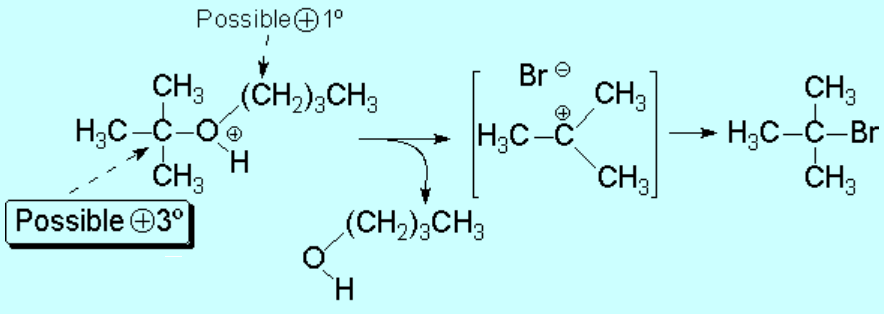
 This is an example of a common technique in Organic Chemistry: Protection of functional groups.
This is an example of a common technique in Organic Chemistry: Protection of functional groups.