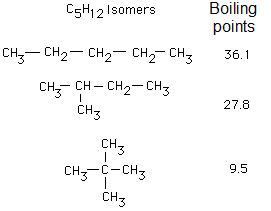
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKANES
The BOILING POINT is the temperature at which a liquid turns into gas. The molecules DON'T BREAK. They only stop attracting one another.
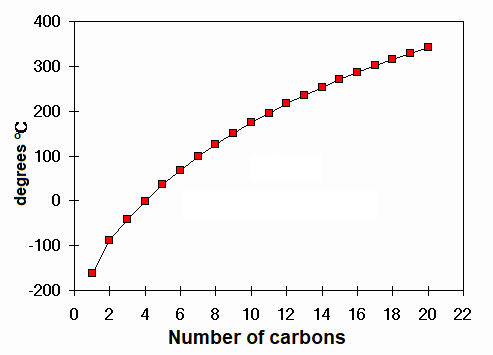 Boling points of linear alkanes
Boling points of linear alkanes
Which is the alkane boiling at 100ºC?
HEPTANE C7H16.
How many atoms does it have?
TWENTY THREE
How many atoms does water have?
Only three, but it also boils at 100ºC too. Why?
The MELTING POINT is the temperature at which a solid melts and transforms into liquid. The molecules DON'T BREAK either. They only 'unpack' from the solid state and attrack each other with more or less strength in the liquid state.
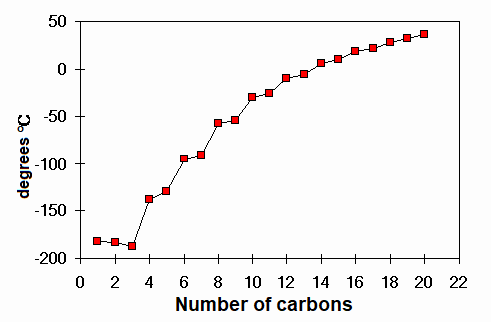 Melting points of linear alkanes
Melting points of linear alkanes
Which alkane melts at 0ºC ?
TRIDECANE C13H28.
How many atoms does it have?
FORTY ONE
How many atoms does water have?
Only three, but it also melts at 0ºC. Why?
The DENSITY allows us to know how compact a compound is at a given temperature.
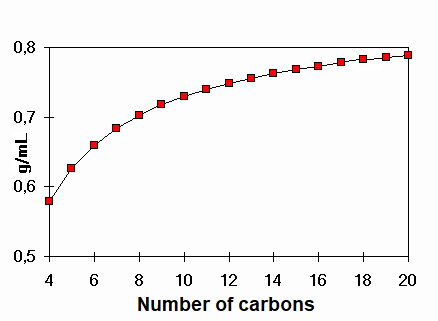 Density of linear alkanes
Density of linear alkanes
Which is the alkane bearing a density of 1 g/mL ?
That value is not reached in the alkane series even with a large number of carbons.
Water, with only three atoms, achieves that density. Why?
The experimental boiling and melting points and the density as well of water suggest that its molecules attract one another with much more strength than alkane molecules do.
The latter need 23 atoms to reach water's boling point, or 40 to achieve water's melting point!!!
 Dispersion forces (London)
Dispersion forces (London)
WEAK
 Dipolar forces
Dipolar forces
STRONG
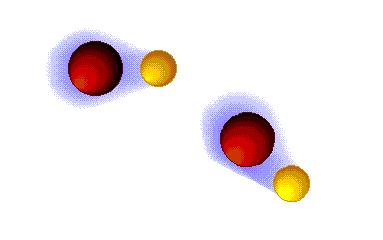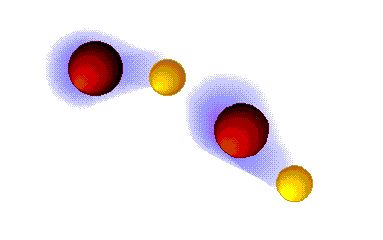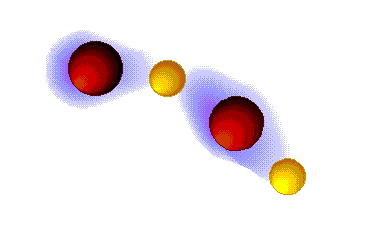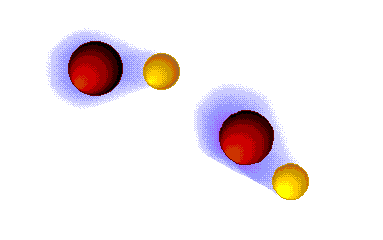 Hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonding
VERY STRONG
The interaction among molecules (INTERMOLECULAR FORCES) is a balance between the repulsion of the external electrons and the attraction of the nuclei of one molecule upon the electrons of the neighboring one.
 Dispersion forces (London)
Dispersion forces (London)
These are the weaker intermolecular forces, the only ones possible in alkanes.
The alkanes, lacking electronegative atoms, have an outer electron shell which is relatively dense and continuous.
The repulsion of the electron clouds is important and the attraction between alkane molecules is thus very weak.
The 'shape' of the molecules affects the contact surface.
What do these experimental results suggest you?
The non-branched molecules, with linear, zig-zag structure attract one another more effectively because their physical constants are higher.
 Boling points of linear alkanes
Boling points of linear alkanes
 Melting points of linear alkanes
Melting points of linear alkanes
 Density of linear alkanes
Density of linear alkanes
 Dispersion forces (London)
Dispersion forces (London) Dipolar forces
Dipolar forces Hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonding Dispersion forces (London)
Dispersion forces (London)